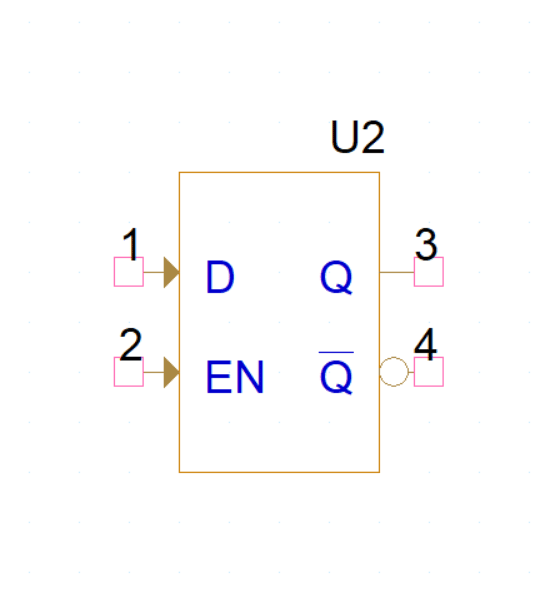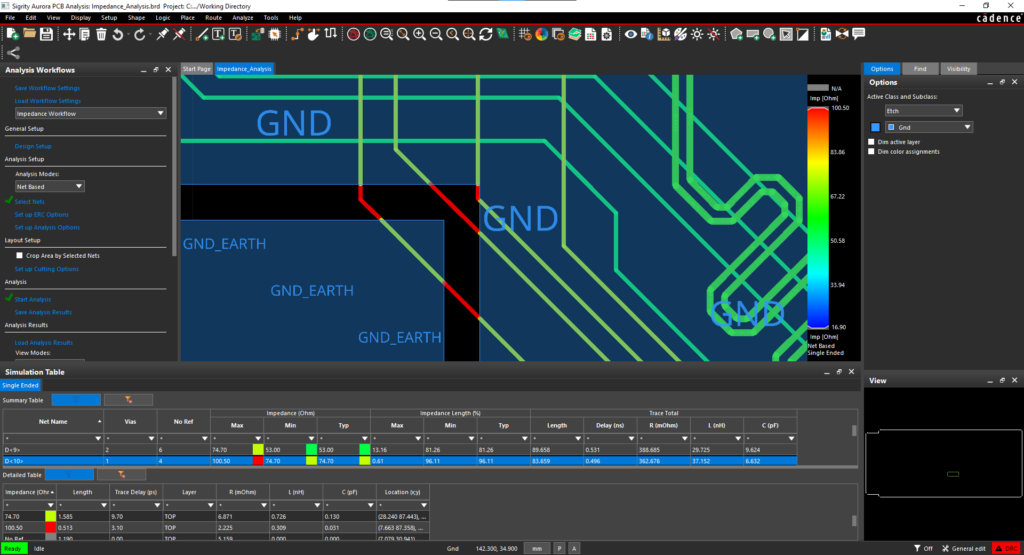
Mixed signal circuit design applications span a range of industries due to the ability to efficiently handle analog and digital signals within the same integrated circuit (IC). Achieving the desired IC functionality and performance requires a deep understanding of the characteristics, constraints, and design considerations of analog, digital, and mixed signal circuits. Below, you will find a comparison of the design needs and challenges for these circuit types.
Comparison of Analog, Digital, and Mixed-Signal Circuit Design Requirements | |||
Design Requirement | Analog Circuits | Digital Circuits | Mixed Signal Circuits |
Signal Integrity | Critical for maintaining signal fidelity and accuracy | Essential to ensure noise immunity and reliable logic operation | Crucial for accurate analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion |
Power Consumption | Emphasis on low power consumption | Power consumption efficiency, especially in high-speed designs | Need for balance between low power consumption and high performance across analog and digital domains |
Susceptible to noise, requiring shielding and filtering | Robust against noise and interference, especially in high-speed environments | Management of both analog and digital noise needed to ensure reliable operation | |
Precision | High precision in component values and amplifiers | Precision in digital logic design and timing | Precision in both analog and digital components for accurate signal processing |
Speed and Timing | Less emphasis on speed, more on signal integrity | Crucial timing considerations for synchronization and operation | Optimization of timing across analog and digital domains |
Layout critical to minimize parasitic effects | Proper layout and routing techniques to minimize propagation delays and crosstalk | Correct layout to separate analog and digital sections while maintaining signal integrity | |
Temperature Stability | Stability across temperature ranges important | Less affected by temperature variations | Stability of both analog and digital components across temperature changes needed |
Filtering and Signal Conditioning | Filtering and conditioning of signals required | Not applicable | Integration of filtering and conditioning for accurate signal processing required |
Logic Design | Not applicable | Logic design essential for implementing functions | Integration of analog and digital logic for mixed-signal processing critical |
Testing and Verification | Comprehensive testing to ensure signal fidelity | Testing focused on logic operation and timing | Testing across analog and digital domains to verify performance and accuracy |
Mixed Signal Circuit Design
Mixed signal circuit design is pervasive across various industries and applications due to its ability to efficiently handle analog and digital signals within the same integrated circuit. Here are a few examples:
- Test and Measurement Equipment: Oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, multimeters, and other test and measurement tools require mixed signal circuitry to handle analog and digital signals.
- Embedded Systems: It is common for embedded systems, such as microcontrollers and digital signal processors, to incorporate mixed-signal circuitry to communicate with the external world, obtain sensor inputs, and control analog peripherals.
- Sensors: Sensors use mixed signal circuits to convert analog outputs into digital signals for processing by microcontrollers or other digital systems. Applications such as industrial automation, automotive systems, and IoT devices commonly use this technology.
- Power Management: From mobile phones to industrial power supplies, power management circuits often need mixed signal design for efficient conversion, regulation, and monitoring of power levels.
- Communication Systems: In communication systems, such as modems, transceivers, and baseband processing units, mixed signal circuits are used to digitize analog signals, such as audio and video. In addition, these circuits are used in Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, where analog RF signals need to be processed and modulated/demodulated digitally for transmission and reception.
- Consumer Electronics: Mixed signal circuitry is used in many consumer electronics products, including smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, and wearable devices for audio processing, touchscreen interfaces, and power management.
- Data Converters: Audio systems, instrumentation, and sensor interfaces rely on mixed signal circuit design for analog-to-digital converters and digital-to-analog converters.
- Automotive Electronics: Mixed signal circuits are used in automotive applications such as engine control units, safety systems, infotainment systems, and sensor interfaces for anti-lock braking systems and airbag deployments.
- Medical Devices: For patient monitoring, diagnostic imaging, and drug delivery systems, mixed signal circuits process analog sensor inputs digitally for analysis or control.
When it comes to circuit design, it is imperative to have the best design and development software tools and expertise on your side. For mixed signal circuit design applications, effective simulation software capabilities are required for efficient development and to ensure performance objectives will be met. Partnering with an industry leader with experience and expertise in providing engineers with these solutions is the best option.
EMA Design Automation is a leading provider of the resources that engineers rely on to accelerate innovation. We provide solutions that include PCB design and analysis packages, custom integration software, engineering expertise, and a comprehensive academy of learning and training materials, which enable you to create more efficiently. For more information on mixed signal circuit design and how we can help you or your team innovate faster, contact us.